 |
|
Image courtesy of Siemens Medical. |
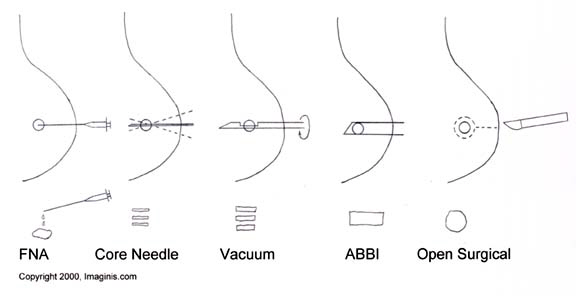
Several methods of breast biopsy now exist. The most appropriate method of biopsy for a patient depends upon a variety of factors, including the size, location, appearance and characteristics of the breast abnormality. Click on one of the biopsy methods below for a detailed explanation of the procedure.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
- Core Needle Biopsy
- Vacuum-Assisted Biopsy (Mammotome or MIBB)
- Large Core Biopsy (ABBI)
- Open Surgical Biopsy (Excisional and Incisional)
|
Summary of Breast Biopsy Methods | |||||
| Type | Used For | Needle Sample size | Anesthesia | Pros | Cons |
| Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) | Cysts; sometimes also used to sample cells from masses with or without calcifications | 22 or 25 gauge needle; several (5-6) samples of fluids and/or cells are removed | Local or none | Fastest and easiest method; results rapidly available; no stitches or scar; excellent for cysts | Small sample size may cause incomplete assessment or misdiagnosis; multiple needle insertions; operator dependent |
| Core Needle | Sample tissue from solid mass or calcium deposits | 10, 11, or 14 gauge needle; several (5-6) samples are removed | Local | Larger sample than FNA can lead to more accurate diagnosis; no stitches or internal scar | Multiple needle insertions; limited sample size may underestimate more serious diagnosis |
| Vacuum-Assisted (Mammotome or MIBB) | Primarily used for calcifications | 11 or 14 gauge needle. Requires 0.25 inch incision (approx. 0.6 cm); several (8-10) samples are removed | Local | Excellent for calcium deposits; removes several large samples with one needle insertion; no stitches; minimal scar | May be less accurate than surgical biopsy which removes entire lesion; not ideal for hard-to-reach lesions (i.e., near chest wall); operator dependent |
| Large Core Surgical (ABBI) | Primarily used for nonpalpable (unable to feel) masses and/or calcifications | 5mm-20mm to cylinder of breast tissue is removed (approx. size and shape of wine cork) | Local | Provides large sample without heavy sedation (as with surgical biopsy) | Removes large amount of normal tissue before reaching lesion, may not remove adequate margin of tissue around lesion; requires stitches; scar |
| Open Surgical | Masses, hard-to-reach lesions, (i.e. near chest wall) multiple lesions; masses with micro-calcifications | Requires 1.5 to 2 inch incision (approx. 4.0 to 5.0 cm); golf ball size area of tissue or more is removed | Heavy sedation; sometimes general anesthesia | Yields largest tissue sample; most accurate method of diagnosis (near 100%) | Causes permanent scar that may make future mammograms difficult to read; possible breast disfigurement; requires stitches and longer recovery |
Updated: May 4, 2008



