Tests to confirm coronary artery disease (CAD) may be ordered if a patient experiences symptoms or if age or family history warrant further examination. Angina (chest pain) and/or dyspnea (shortness of breath) may accompany CAD. Other symptoms include tightness, heaviness, burning sensation, pressure, squeezing, or pain behind the breastbone or less commonly pain also in the arms, neck or jaws, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, sweating, or weakness.
Diagnostic Tests Used to Confirm CAD
 |
|
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): An electrocardiogram is a graphical record of the electrical activity of the heart. A normal ECG, in most cases, rules out the presence of other cardiac diseases. An abnormal ECG indicates the presence of a cardiac disease and further investigations are performed. An ECG can be beneficial in detecting the disease and sometimes even the extent of the disease.
- Stress test: A stress test involves taking an ECG before, during and after a treadmill workout to detect cardiac disease and/or damage, including the extent of CAD. However, false positive results are possible with stress tests.
- Echocardiogram (heart ultrasound): This diagnostic technique is an excellent tool to provide details of the cardiac structures – vessels, valves, and muscle. Echocardiography is a non-invasive exam in which images are acquired and viewed in real time without the use of radiation. Echocardiography is often useful in studying the beating heart and provides some information on functional abnormalities of the heart wall, valves and blood vessels. Echocardiography with Doppler is used to measure blood flow across valves, across septal defects (shunts), extent of regurgitations, etc. Color flow mapping capability is extremely useful in the detection of shunts. Abnormal operation of the valves can be detected by studying the opening and closing function versus normal valve function. Echocardiography may also be used to study congenital heart defects such as a septal defect (a hole in the wall that separates the two chambers of the heart).
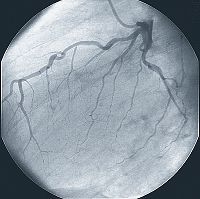
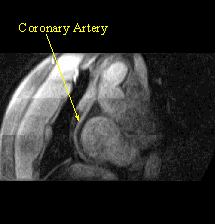
- Nuclear cardiology: Nuclear cardiology (also called radionuclide scanning or stress thallium imaging) allows visualization of the function of the heart. Myocardial perfusion imaging is the most common nuclear cardiology test to assess CAD. This noninvasive test can identify and quantify areas of inadequate blood supply within the myocardium (heart muscle), detect scaring of the myocardium, and assess the heart's pumping function. Nuclear cardiology is a cost-effective tool to help determine which patients are candidates for coronary angiography, revascularization, or coronary artery bypass surgery. Nuclear cardiology is also useful to monitoring the effectiveness of coronary revascularization or bypass surgery.
- Ambulatory monitoring: If no abnormality, disease or damage is detected and the patient still feels uneasy when performing stressful activities (such as climbing stairs) but feels okay under normal activity, then an ambulatory monitor may be used. An ambulatory monitor is a portable ECG system (often worn around the waist) that continuously monitors the heart’s electrical activity.
 |
|
 |
|
Updated: February 29, 2008



