Diagnostic imaging refers to a variety of non-invasive methods for identifying and monitoring diseases or injuries via the generation of images representing internal anatomic structures and organs of the patient's body. The detailed images produced by these procedures are used to further inform the patient and physician about the anatomic organization and functional working of the inner organs and structure of the patient's body. Diagnostic imaging is an informational tool that expands the knowledge of physicians, people and patients and the practice of medicine.
 |
 |
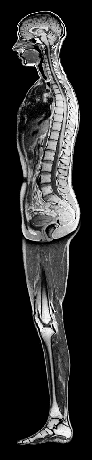
| Reconstructed side view MR (sagittal image) |
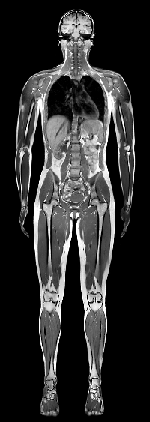
Reconstructed frontal view MR (coronal image) |
Radiologists and other physicians interpret the resulting images to diagnose various medical illness or injury so that patient treatment and therapy can be specifically planned and implemented. Diagnostic imaging is also used to guide surgical plannin g and is often used to follow surgery and/or monitor the outcomes of therapeutic procedures.
Diagnostic imaging denotes that new innovative techniques like ultrasound (US), magnetic resonance (MR) and computed tomography (CT) are now also performed in radiology centers and departments along with traditional x-ray or radiology (see History of Medical Diagnosis and Diagnostic Imaging for more background).
Diagnostic Imaging is a Key Tool in the Early Diagnosis and Prevention of Disease
Of high importance in today's managed care environment, diagnostic imaging can also be used for the early identification of potential medical problems, to help prevent their occurrence. Thus expensive therapeutic treatment may be eliminated to create substantial savings for the patient and healthcare system. In other words, the emergence of so called "disease management" techniques places a premium on diagnostic imaging since the savings accrued by avoiding the very expensive surgery or therapy significantly offsets the cost of the imaging procedure.
New, minimally invasive surgical procedures are emerging which can be performed on an outpatient basis together with the diagnostic imaging procedure, for instance CT, MR or ultrasound. By combining delivery of therapy with the diagnostic procedure, the healthcare system can realize significant savings. More on using non-invasive imaging to guide minimally invasive therapy.
Updated: August 2010



